Microsoft PowerPivot is slowly becoming an essential technology for Business Users addressing Self-Service Business Intelligence. It is innovated by Microsoft SQL Server team as a part of Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 release and comes in two flavors; PowerPivot for Excel and PowerPivot for SharePoint. I have already written a post on Excel add-in (Creating Self-Service Business Intelligence dashboard with PowerPivot – Part I) which discusses dashboard creation with Excel and PowerPivot. This post discusses about Installing PowerPivot for SharePoint 2010 with following sections;
-
Excel and SharePoint
-
Installing PowerPivot for SharePoint 2010
-
Error: Could not load assembly
‘Microsoft.AnalysisServices.SharePoint.Integration.dll’
-
SQL Server Analysis Services Installation – VertiPaq
-
Deploying PowerPivot solution packages to Web Application
-
Other Services required
-
Creating PowerPivot Service Application
-
PowerPivot Feature Integration for Site Collections
-
Configuring PowerPivotUnAttendedAccount for Data Refresh
Excel and SharePoint
Why two technologies? We can consider that Excel is for authoring PowerPivot applications. It allows to create an application with one or many data sources and then facilitates data analysis in a multi-dimensional structure. It does not need a constant connection to used data sources, everything will be stored inside Excel Workbook and if want, data can be refreshed. SharePoint can be considered as a hosting environment for PowerPivot applications. We usually go for SharePoint if collaboration, sharing and reporting are required.
Installing PowerPivot for SharePoint 2010
There are two components need to be installed. PowerPivot System Service and Analysis Services in VertiPaq mode which is a local, in-process Analysis Services engine. Let’s start with Analysis Services.
Installing Analysis Services for PowerPivot is straight forward. I have already set up my SharePoint 2010 farm. It uses SQL Server 2008 R2 that exist in same box. Note that my installation contains full SQL Server product suite, including SQL Server Analysis Services, hence new instance of Analysis Services for PowerPivot will be a named instance. There is a known issue you might face if SQL Server installation is already exist. It is;
Could not load assembly ‘Microsoft.AnalysisServices.SharePoint.Integration.dll’
You get this error if you have a prior installation of SQL Server 2008 R2. Unfortunately it comes at the completion of the installation.
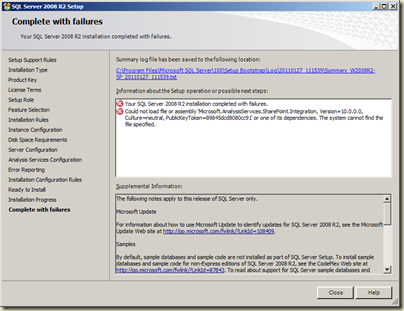
Solution for this is simple. Create a text file as below and save it as Setup100.exe.config.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<runtime>
<disableCachingBindingFailures enabled="1" />
</runtime>
</configuration>
Then move the file into %ProgramFIles%\Microsoft SQL Server\100\Setup Bootstrap\SQLServer2008R2\x64. Once the file is placed, you need to start the installation again. For more information, see this: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2261507 .
SQL Server Analysis Services Installation – VertiPaq
Before starting the installation, make sure that a domain account is created for new Analysis Services instance for running the service. In my case, newly created account for this is PowerPivotAnalysisServices.
Now run the SQL Server 2008 R2 setup. It would be better to run the setup as Administrator (Right click on Setup.exe and select “Run as Administrator”). If you have configured more than one server for the farm as Application Servers, the installation should be done for all servers (Generally we set up two servers one for WFE and another for applications. This installation should be done only on Application Servers).
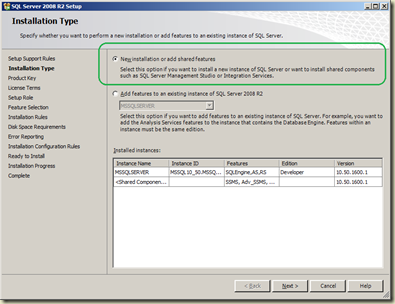
Once the installation is started, select New installation or add shared features as per the screen below.
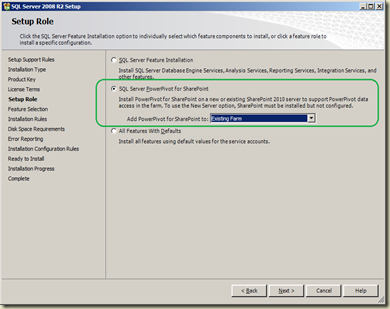
Continue with screens until you get a screen which allows you to select SQL Server PowerPivot for SharePoint. Select Existing Farm for Add PowerPivot for SharePoint to (Note that assumption here is Farm is already configured).
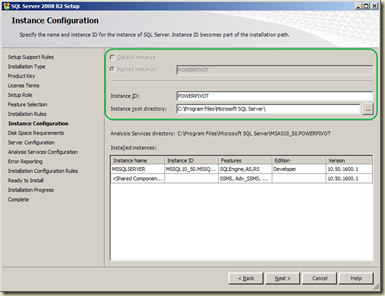
Next screen is Feature Selection. It is a read-only screen, you will not be able to change anything on it. Continue with the wizard until you get Instance Configuration screen. You will notice that the instance has already been named ad POWERPIVOT. Do not change it, continue the wizard.
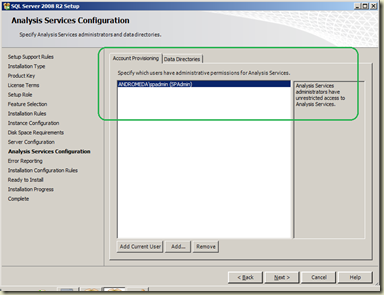
At the Server Configuration screen, set newly created domain account and its password for SQL Server Analysis Services. When you have Analysis Services Configuration screen, make sure that accounts that need to be administrators for Analysis Services are added.
Everything is set now, continue the wizard and complete the installation. Once it is done, go to SharePoint Central Administration –> System Settings –> Manage Servers in this Farm. It shows all the servers in the farm and services running. If you see SQL Server Analysis Services and SQL Server PowerPivot System Service, your installation is successful.
Deploying PowerPivot solution packages to Web Application
Next part is deploying PowerPivot solution packages to Web Applications (to WFE Servers). There are two solution packages. Installation we performed earlier deploys solution packages for Central Administration but not for our web application. Go to SharePoint Central Administration –> System Settings –> Farm Management –> Manage Farm Solutions. You should see two solutions;
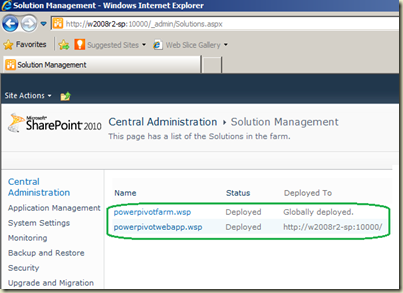
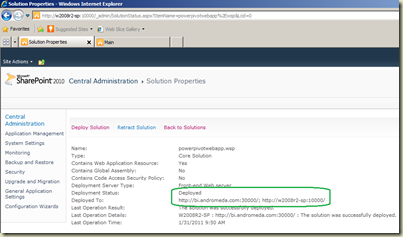
Let’s deploy powerpivotwebapp.wsp to a web application. Click on powerpivotwebapp.wsp. It opens Solution Properties. Click on Deploy Solution. Select the web application from the drop-down you need to use under Deploy to? and click OK. Once the Solution Properties page is open, make sure that added web application is listed as below.
Other Services required
Next step is starting all other necessary services required by PowerPivot. Make sure following services are running;
-
Excel Calculation Service
-
Secure Store Service
-
Claims to Windows token Service
-
SQL Server Analysis Services
-
SQL Server PowerPivot System Service
These services are listed under SharePoint Central Administration –> System Settings –> Manage Services on Servers.
Creating PowerPivot Service Application
This helps to establish the communication between WFE and PowerPivot service via PowerPivot Service Application Proxy. Let’s create it. Go to SharePoint Central Administration –> Application Management –> Manage Service Applications. Click on New and select SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application.
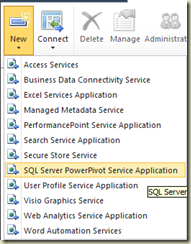
With Create New PowerPivot Service Application window, set the name as PowerPivotServiceApplication. Do not use any existing pool, create a new one and assign a domain account for it. Set the database server and database name then. Finally select the checkbox Add the proxy for this PowerPivot service application to the default proxy group. Click OK to create it.
PowerPivot Feature Integration for Site Collections
This is appeared under Site Collection Features and must be activated for each of the site collections. Go to your site collection and click on Site Actions –> Site Settings –> Site Collection Administration –> Site Collection Features. When the page open, find PowerPivot Services feature integration for Site Collections and activate it.
Configuring PowerPivotUnAttendedAccount for Data Refresh
PowerPivot unattended account is used for refreshing data in the workbook if user credentials are not exist with the workbook. This account is stored in SharePoint Secure Store Service. In order to continue, you need to make sure that Secure Store Service is up and running, and master key is created. I have already configured Secure Store Service for PerformancePoint. If you have not, see this post for configuring it: http://dinesql.blogspot.com/2010/07/configuring-performancepoint-2010.html.
Let’s open the Secure Store Service Application. Go to SharePoint Central Administration –> Application Management –> Manage Service Applications. Click on Secure Store Service (or select it and click on Manage) link;
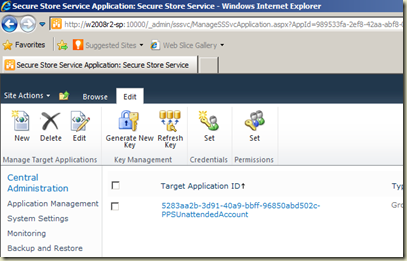
Secure Store Service uses Target Applications for holding accounts. In my case, I have an application set up for PerformancePoint and that is what has been listed. If you have note, nothing will be listed. Once a Target Application is created for PowerPivot, it has to be associated with PowerPivot Service Application. Let’s start creating the Target Application. Click on New for opening Create New Secure Store Target Application. Set ID and name for the application. Appropriate ID and name would be PowerPivotDataRefresh and Power Pivot Data Refresh. Enter a valid email for Contact Email and select Individual for Target Application Type.
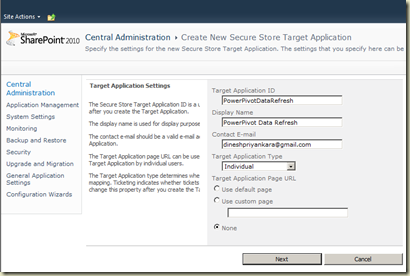
Next screen for specifying fields (columns) for the application. Accept the default as we need only user name and password and continue.
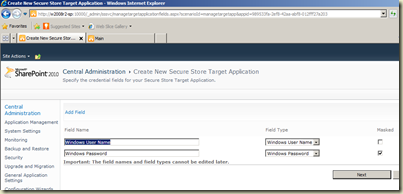
Next screen for setting admins for the application. Make sure that you have added the account which is used for PowerPivot Service Application pool. In addition to that, any account need to be an admin can be added. Continue the wizard and complete. Finally you are back on Secure Store Service. You should see the newly created application listed now.
Next is setting credentials for PowerPivotDataRefresh application (or PowerPivot unattended account). Select the check box next to newly created application and click on Set Credentials button. It opens the Set Credentials for Secure Target Application (Individual). Settings for this screen will be;
-
Credential Owner: This is the owner of the credential. It will be used by PowerPivot unattended account but this is not the account used as the unattended account.
-
Windows user name and password: This is the actual account used as the unattended account.
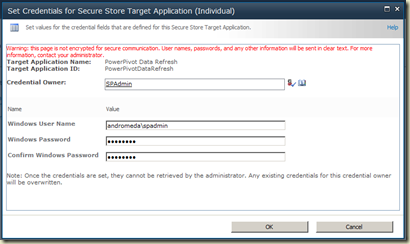
Click OK. Now we need to associate the application with PowerPivot Service Application. Go to SharePoint Central Administration –> Application Management –> Manage Service Applications. Find PowerPivot Service Application and click the link (or select it and click on Manage button). This opens PowerPivot Management Dashboard. Click on Configure Service Application Settings in Actions frame. It opens PowerPivot Settings. Find PowerPivot Unattended Data Refresh Account input box under Data Refresh. Type the ID of the application created in Secure Store Service, in my case, it is PowerPivotDataRefresh.
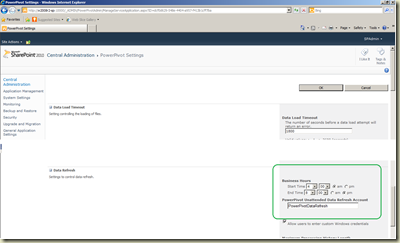
Done. To complete the process, few setting have to be done in Excel Services.
Settings in Excel Services
Go to SharePoint Central Administration –> Application Management –> Manage Service Applications. Find Excel Services Application and open it. It opens Manage Excel Services Application. Click on Trusted File Locations.
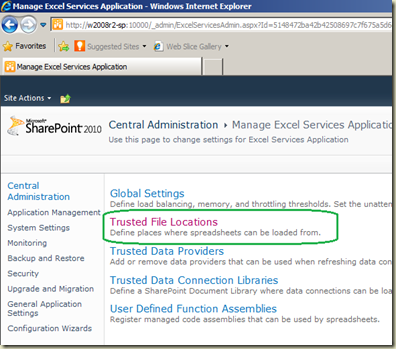
You will see that SharePoint has been added as a Trusted Location (Address is http://). In order to access a workbook by both Excel and PowerPivot services, this is required.
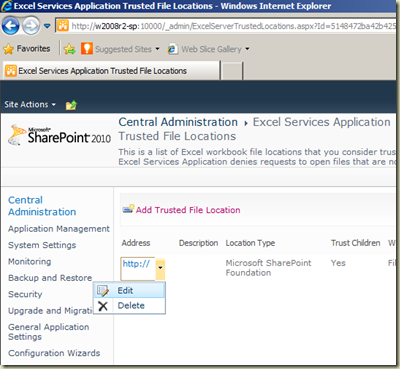
Get the menu of http:// and select Edit. Change following items in Edit Trusted File Location.
-
Workbook Properties: Maximum Workbook Size. Set as you want. Note that maximum file size accepted by SharePoint for both Excel and PowerPivot is 2GB.
-
External Data: Select Trusted data connection libraries and embedded under Allow External Data.
Click OK to save settings. Now, You should be able to upload an Excel file that contains PowerPivot data into the web application and see.
Will discuss more on this in another post.